浅拷贝和深拷贝
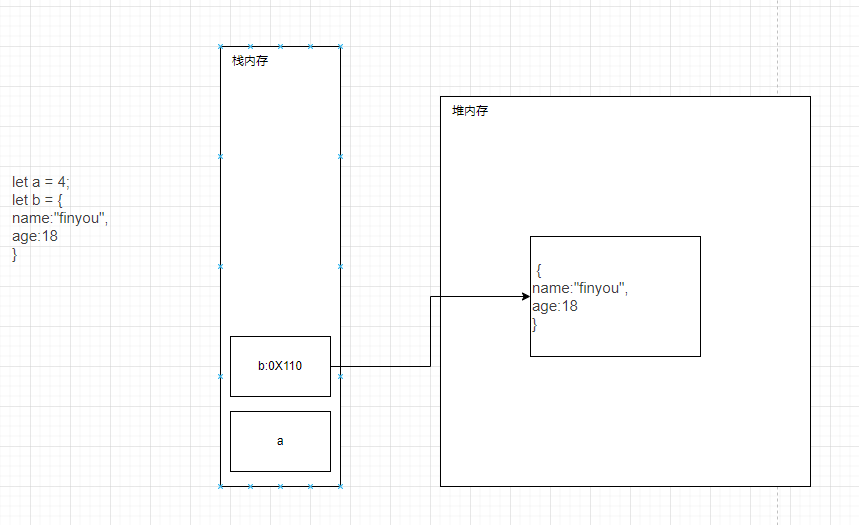
数据类型
js中存在俩大数据类型:
基本数据类型保存在栈内存
引用数据类型保存在堆内存中,引用数据类型的变量存在栈中,在栈中保存一个地址指向堆内存中

浅拷贝
浅拷贝:创建一个新的数据,这个数据对原始数据进行拷贝:
实现一个浅拷贝
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| function shallowClone(obj) {
const newObj = {};
for(let prop in obj) {
if(obj.hasOwnProperty(prop)){
newObj[prop] = obj[prop];
}
}
return newObj;
}
const objA = {
name: 'finyou',
age: 18,
address: {
x: 100,
y: 200,
c:{
less:1000
}
}
}
let newObjA = shallowCopy(objA);
objA.address.c.less = 'finyou'
objA.age = 24
console.log(newObjA.address.c.less);
console.log(newObjA.age)
|
当我们改变复制的一层,改变的值没发生改变,当我么改变深层的值,改变的值改变。
其他实现浅拷贝的方式
1.Object.assign
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| var obj = {
age: 18,
nature: ['smart', 'good'],
names: {
name1: 'fx',
name2: 'xka'
},
love: function () {
console.log('fx is a great girl')
}
}
var newObj = Object.assign({}, obj);
obj.names.name1 = 'xka';
console.log(newObj);
|
2.Array.prototype.slice(),Array.prototype.concat()
slice()
1
2
3
4
5
| const fxArr = ["One", "Two", "Three"]
const fxArrs = fxArr.slice(0)
fxArrs[1] = "love";
console.log(fxArr)
console.log(fxArrs)
|
concat()
1
2
3
4
5
| const fxArr = ["One", "Two", "Three"]
const fxArrs = fxArr.concat()
fxArrs[1] = "love";
console.log(fxArr)
console.log(fxArrs)
|
3.使用拓展运算符实现的复制
1
2
3
4
5
| const fxArr = ["One", "Two", "Three"]
const fxArrs = [...fxArr]
fxArrs[1] = "love";
console.log(fxArr)
console.log(fxArrs)
|
浅比较
在React中,类组件的继承中有React.Component和React.PureComponent中,采用浅比较来实现shouldComponentUpdate,当组件的props或state发生变化时,只有当值或引用地址改变时,组件才会更新
浅比较:只比较对象的一层,深层次只比较引用地址
实现一个浅比较的函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| const isObject = (obj)=>{
return obj !== null && typeof obj === 'object';
}
const shallowEqual = (objA, objB) => {
if(!isObject(objA) && !isObject(objB)) return false;
if(Object.is(objA,objB)) return true;
const keyarrayA = Reflect.ownKeys(objA);
const keyarrayB = Reflect.ownKeys(objB);
if(keyarrayA.length !== keyarrayB.length) return false;
for(let key in objA){
if(!objB.hasOwnProperty(key) || !Object.is(objA[key],objB[key])){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
|
深拷贝
深拷贝开辟一个新的栈,两个对象属完成相同,但是对应两个不同的地址,修改一个对象的属性,不会改变另一个对象的属性
JSON.stringify()
JSON.stringify()会忽略undefined、symbol和函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| const obj = {
name: 'A',
name1: undefined,
name3: function() {},
name4: Symbol('A')
}
const obj2 = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(obj));
console.log(obj2);
|
循环递归
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| function deepClone(obj, hash = new WeakMap()) {
if (obj === null) return obj;
if (obj instanceof Date) return new Date(obj);
if (obj instanceof RegExp) return new RegExp(obj);
if (typeof obj !== 'object') return obj;
if (hash.get(obj)) return hash.get(obj);
let cloneObj = new obj.constructor();
hash.set(obj, cloneObj);
for (let key in obj) {
if (obj.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
cloneObj[key] = deepClone(obj[key], hash);
}
}
return cloneObj;
}
|